Pyogenic liver abscess
Definition
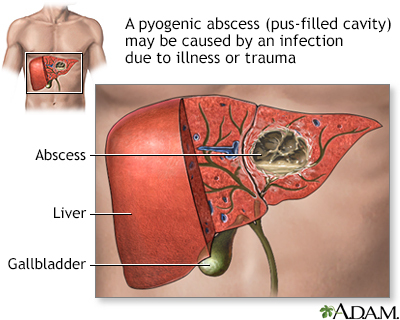
Pyogenic liver abscess is a pus-filled pocket of fluid within the liver. Pyogenic means "with pus".
Alternative Names
Liver abscess; Bacterial liver abscess; Hepatic abscess
Causes
There are many possible causes of liver abscesses, including:
- Abdominal infection, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, or a perforated bowel
- Infection in the blood
- Infection of the tubes draining bile (bile ducts)
- Recent endoscopy of the bile draining tubes
- Trauma that damages the liver
A number of common bacteria may cause liver abscesses. In most cases, more than one type of bacteria are found.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver abscess may include:
- Pain in the right upper abdomen (more common) or throughout the abdomen (less common)
- Clay-colored stools
- Dark urine
- Fever, chills, night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting
- Unintentional weight loss
- Weakness
- Yellow skin (jaundice)
- Right shoulder pain (referred pain)
- Chest pain (lower right)
Exams and Tests
Tests may include:
Treatment
Treatment usually consists of placing a tube through the skin into the liver to drain the abscess. Less often, surgery is needed. You will also receive antibiotics for about 4 to 6 weeks. Sometimes, antibiotics alone can cure the infection.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This condition can be life threatening. The risk for death is higher in people who have many liver abscesses.
Possible Complications
Life-threatening sepsis can develop. Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have:
- Any symptoms of this disorder
- Severe abdominal pain
- Confusion or decreased consciousness
- High fever that doesn't go away
- Other new symptoms during or after treatment
Prevention
Prompt treatment of abdominal and other infections may reduce the risk of developing a liver abscess, but most cases are not preventable.
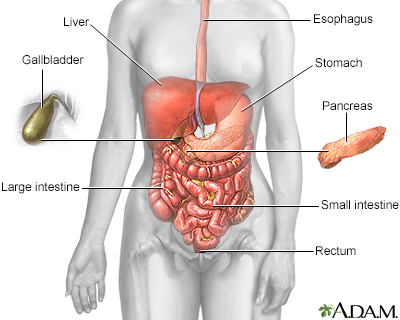
Gallery
References
Kim AY, Chung RT. Bacterial, parasitic, and fungal infections of the liver, including liver abscesses. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 84.
Sifri CD, Madoff LC. Infections of the liver and biliary system (liver abscess, cholangitis, cholecystitis). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 75.