Lymphadenitis
Definition
Lymphadenitis is an infection of the lymph nodes (also called lymph glands). It is a complication of certain bacterial infections.
Alternative Names
Lymph node infection; Lymph gland infection; Localized lymphadenopathy
Causes
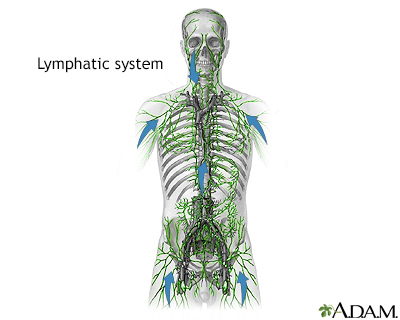
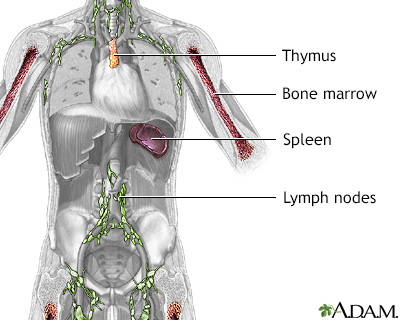
The lymph system (lymphatics) is a network of lymph nodes, lymph ducts, lymph vessels, and organs that produce and move a fluid called lymph from tissues to the bloodstream.
The lymph glands, or lymph nodes, are small structures that filter the lymph fluid. There are many white blood cells in the lymph nodes to help fight infection.
Lymphadenitis occurs when the glands become enlarged by swelling (inflammation), often in response to bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The swollen glands are usually found near the site of an infection, tumor, or inflammation.
Lymphadenitis may occur after skin infections or other infections caused by bacteria such as streptococcus or staphylococcus. Sometimes, it is caused by rare infections such as tuberculosis or cat scratch disease (bartonella).
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Red, tender skin over lymph node
- Swollen, tender, or hard lymph nodes
- Fever
Lymph nodes may feel rubbery if an abscess (pocket of pus) has formed or they have become inflamed.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This includes feeling your lymph nodes and looking for signs of injury or infection around any swollen lymph nodes.
A biopsy and culture of the affected area or node may reveal the cause of the inflammation. Blood cultures may reveal spread of infection (often bacteria) to the bloodstream.
Treatment
Lymphadenitis may spread within hours. Treatment should begin right away.
Treatment may include:
- Antibiotics to treat any bacterial infection
- Analgesics (painkillers) to control pain
- Anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce inflammation
- Cool compresses to reduce inflammation and pain
Surgery may be needed to drain an abscess.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Prompt treatment with antibiotics usually leads to a complete recovery. It may take weeks, or even months, for swelling to disappear.
Possible Complications
Untreated lymphadenitis may lead to:
- Abscess formation
- Cellulitis (a skin infection)
- Fistulas (seen in lymphadenitis that is due to tuberculosis)
- Sepsis (bloodstream infection), which can lead to death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or go to the emergency room if you have symptoms of lymphadenitis.
Prevention
Good general health and hygiene are helpful in the prevention of any infection.
Gallery
References
Pasternack MS. Lymphadenitis and lymphangitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 95.