Cataract removal
Definition
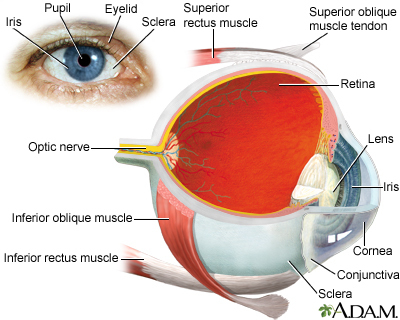
Cataract removal is surgery to remove a clouded lens (cataract) from the eye. Cataracts are removed to help you see better. The procedure almost always includes placing an artificial lens (IOL) in the eye.
Alternative Names
Cataract extraction; Cataract surgery
Description
Patient Education Video: Cataracts
Cataract surgery is an outpatient procedure. This means you likely do not have to stay overnight at a hospital. The surgery is performed by an ophthalmologist. This is a medical doctor who specializes in eye diseases and eye surgery.
Adults are usually awake for the procedure. Numbing medicine (local anesthesia) is given using eyedrops or a shot to block pain. You will also get medicine to help you relax. Children usually receive general anesthesia. This is medicine that puts them into a deep sleep so that they are unable to feel pain.
The doctor uses a special microscope to view the eye. A small cut (incision) is made in the eye.
The lens is removed in one of the following ways, depending on the type of cataract:
- Phacoemulsification: With this procedure, the doctor uses a tool that produces sound waves to break up the cataract into small pieces. The pieces are then suctioned out. This procedure uses a very small incision.
- Extracapsular extraction: The doctor uses a small tool to remove the cataract in mostly one piece. This procedure uses a larger incision.
- Laser surgery: The doctor guides a machine that uses laser energy to make the incisions and soften the cataract. The rest of the surgery is much like phacoemulsification. Using the laser instead of a knife (scalpel) may speed recovery and be more accurate.
After the cataract is removed, a manmade lens, called an intraocular lens (IOL), is usually placed into the eye to restore the focusing power of the old lens (cataract). It helps improve your vision. Depending on the power of the IOL and the type implanted, glasses may not be needed after surgery.
The doctor may close the incision with very small stitches. Usually, a self-sealing (sutureless) method is used. If you have stitches, they may need to be removed later.
The surgery lasts less than half an hour. Most times, just one eye is done. If you have cataracts in both eyes, your doctor may suggest waiting at least 1 to 2 weeks between each surgery. Recently, some health systems have performed surgery in both eyes, just minutes apart.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
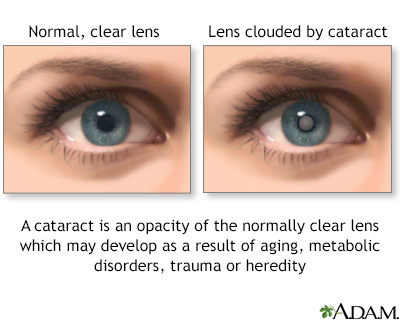
The normal lens of the eye is clear (transparent). As a cataract develops, the lens becomes cloudy. This blocks light from entering your eye. Without enough light, you cannot see as clearly.
Cataracts are painless. They are most often seen in older adults. Sometimes, children are born with them. Cataract surgery is usually done if you cannot see well enough because of cataracts. Cataracts usually do not permanently damage your eye, so you and your eye doctor can decide when surgery is right for you.
Risks
In rare cases, the entire lens cannot be removed. If this happens, a procedure to remove all of the lens fragments will be done at a later time. Afterward, vision can still be improved.
Very rare complications can include infection and bleeding. This can lead to permanent vision problems.
Before the Procedure
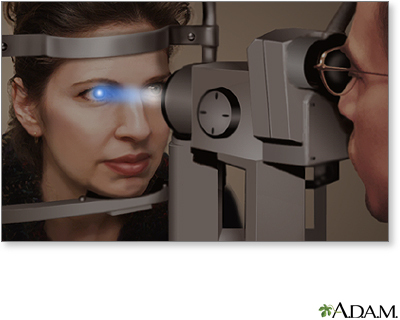
Before surgery, you will have a complete eye exam and eye tests by the ophthalmologist.
The doctor will use ultrasound or a laser scanning device to measure your eye. These tests help determine the best IOL for you. Usually, the doctor will try to choose an IOL that can allow you to see without glasses or contact lenses after surgery. Some IOLs give you both distance and near vision, but they are not for everyone. Ask your doctor which one is best for you. Be sure you understand what your vision will be like after the IOL is implanted. Also, be sure to ask questions so that you will know what to expect of the surgery.
Your doctor may prescribe eyedrops before the surgery. Follow instructions exactly on how to use the drops.
After the Procedure
Before you go home, you may receive the following:
- A patch to wear over your eye until the follow-up exam
- Eyedrops to prevent infection, treat inflammation, and help with healing
You will need to have someone drive you home after surgery.
You will usually have a follow-up exam with your doctor the next day. If you had stitches, you will need to make an appointment to have them removed.
Tips for recovering after cataract surgery:
- Wear dark sunglasses outside after you remove the patch.
- Wash your hands well before and after using eyedrops and touching your eye. Try not to get soap and water in your eye when you are bathing or showering for the first few days.
- Light activities are best as you recover. Check with your doctor before doing any strenuous activity, resuming sexual activity, or driving.
Recovery takes about 2 weeks. If you need new glasses or contact lenses, you can usually have them fitted at that time. Keep your follow-up visit with your doctor.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people do well and recover quickly after cataract surgery.
If a person has other eye problems, such as glaucoma or macular degeneration, the surgery may be more difficult or the outcome may not be as good.
Gallery

References
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Cataract /Anterior Segment Summary Benchmark - 2020, AAO PPP Cataract and Anterior Segment Panel, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care. www.aao.org/summary-benchmark-detail/cataract-anterior-segment-summary-benchmark-2020. Updated December 2020. Accessed September 2, 2021.
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Preferred Practice Patterns Cataract and Anterior Segment Panel, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care. Cataract in the adult eye PPP - 2021. www.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/cataract-in-adult-eye-ppp-2021-in-press. Updated November 2021. Accessed September 2, 2021.
Salmon JF. Lens. In: Salmon JF, ed. Kanski's Clinical Ophthalmology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 10.
Tipperman R. Cataracts. In: Gault JA, Vander JF, eds. Ophthalmology Secrets in Color. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 21.
