Bone lesion biopsy
Definition
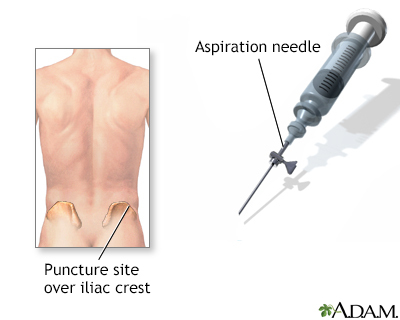
A bone lesion biopsy is the removal of a piece of bone or bone marrow for examination.
Alternative Names
Bone biopsy; Biopsy - bone
How the Test is Performed
The test is done in the following way:
- An x-ray, CT or MRI scan is likely used to guide the exact placement of the biopsy instrument.
- The health care provider applies a numbing medicine (local anesthetic) to the area.
- A small cut is then made in the skin.
- A special drill needle is often used. This needle is gently inserted through the cut, then pushed and twisted into the bone.
- Once the sample is obtained, the needle is twisted out.
- Pressure is applied to the site. Once bleeding stops, stitches are applied, and covered with a bandage.
- The sample is sent to a lab for examination.
Bone biopsy may also be done under general anesthesia to remove a larger sample. Then surgery to remove the bone can be done if the biopsy exam shows that there is an abnormal growth or cancer.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow your health care provider's instructions on how to prepare. This may include not eating and drinking for several hours before the procedure. If you take any blood thinners, please make sure you stop them ahead of the procedure.
How the Test will Feel
With a needle biopsy, you may feel some discomfort and pressure, even though a local anesthetic is used. You must remain still during the procedure.
After the biopsy, the area may be sore or tender for several days.
Why the Test is Performed
The most common reasons for bone lesion biopsy are to tell the difference between cancerous and noncancerous bone tumors and to identify other bone or bone marrow problems. It may be performed on people with bone pain and tenderness, particularly if x-ray, CT scan, or other testing reveals a problem.
Normal Results
No abnormal bone tissue is found.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may be any of the following problems.
Benign (noncancerous) bone tumors, such as:
- Bone cyst
- Fibroma
- Osteoblastoma
- Osteoid osteoma
Cancerous tumors, such as:
- Ewing sarcoma
- Multiple myeloma
- Osteosarcoma
- Other types of cancer that may have spread to the bone
Abnormal results may also be due to:
- Osteitis fibrosa (weak and deformed bone)
- Osteomalacia (softening of the bones)
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
- Bone marrow disorders (leukemia or lymphoma)
Risks
Risks of this procedure may include:
- Bone fracture
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Damage to surrounding tissue
- Discomfort
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection near the biopsy area
A serious risk of this procedure is bone infection. Signs include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Worsening pain
- Redness and swelling of around the biopsy site
- Drainage of pus from the biopsy site
If you have any of these signs, contact your provider right away.
People with bone disorders who also have blood clotting disorders may have an increased risk of bleeding.
Gallery
References
Katsanos K, Sabharwal T, Cazzato RL, Gangi A. Skeletal interventions. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 87.
Schwartz HS, Holt GE, Halpern JL. Bone tumors. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 33.
Schwartz HS, Holt GE, Halpern JL. Interventional radiologic techniques in management of bone tumors. In: Heymann D, ed. Bone Cancer. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 33.
