Avoiding anorexia of aging
A nibble of toast, a bite of apple, and grandma says she’s full. You may have noticed this phenomenon: As they age, between 15 and 20 percent of older adults develop appetite loss that...
Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
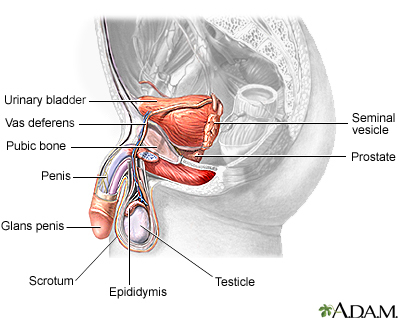
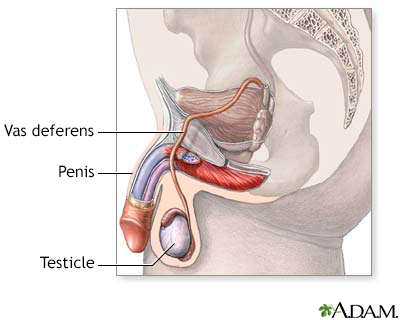
Anorchia is the absence of both testes at birth.
Vanishing testes - anorchia; Empty scrotum - anorchia; Scrotum - empty (anorchia)
The embryo develops early sex organs in the first several weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, early testes do not develop in males before 8 weeks into the pregnancy. These babies will be born with female sex organs.
In some cases, the testes disappear between 8 and 10 weeks. These babies will be born with ambiguous genitalia. This means the child will have parts of both male and female sex organs.
In some cases, the testes may disappear between 12 and 14 weeks. These babies will have normal penis and scrotum. However, they will not have any testes. This is known as congenital anorchia. It is also called the "vanishing testes syndrome."
The cause is unknown. Genetic factors may be involved in some cases.
This condition should not be confused with bilateral undescended testes, in which the testes are located in the abdomen or groin rather than the scrotum.
Symptoms may include:
Signs include:
Tests include:
Treatment includes:
The outlook is good with treatment.
Complications include:
Contact your health care provider if a male child:
Ali O, Donohoue PA. Hypofunction of the testes. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 601.
Chan Y-M, Hannema SE, Achermann JC, Hughes IA. Disorders of sex development. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 24.
Yu RN, Diamond DA. Disorders of sexual development: etiology, evaluation, and medical management. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 48.
A nibble of toast, a bite of apple, and grandma says she’s full. You may have noticed this phenomenon: As they age, between 15 and 20 percent of older adults develop appetite loss that...
Advertisers and celebrities are often blamed for perpetuating the myth that women aren’t attractive unless they’re thin. Critics say...